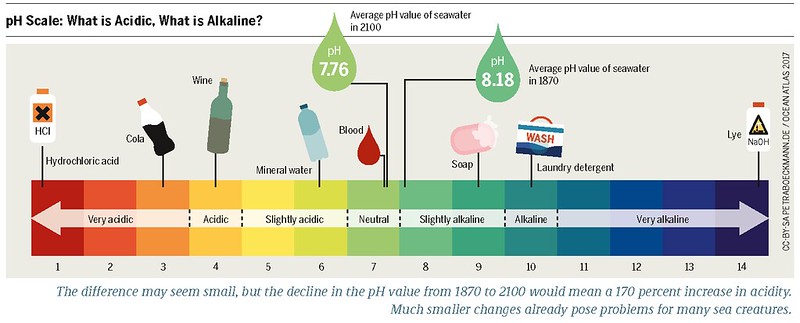
The pH of boric acid in water is a crucial factor to consider, especially for DIY users who want to balance its pH level for various applications. Boric acid, chemically known as H3BO3, has a pKa value of 9.15, which means it exists as undissociated boric acid in aqueous solutions at or below pH 7. Above pH 10, the metaborate anion dominates.
Understanding the pH of Boric Acid in Water
When boric acid is dissolved in water, it partially dissociates to give metaboric acid, with boric acid predominating in solution below pH 9. This buffer capacity is particularly useful in swimming pools or ocean waters, where it can substitute for the bicarbonate system with a pKa of around 9.0.
Factors Affecting the pH of Boric Acid in Water
-
Concentration of Boric Acid: The pH of boric acid in water is influenced by the concentration of the acid. Higher concentrations of boric acid will result in a lower pH, while lower concentrations will lead to a higher pH.
-
Temperature: The pH of boric acid in water can also be affected by temperature. As the temperature increases, the pH of the solution may decrease slightly.
-
Presence of Other Substances: The presence of other substances in the water, such as salts or other acids/bases, can also influence the pH of the boric acid solution.
Balancing the pH of Boric Acid in Water
For DIY users, it’s essential to understand how to balance the pH of boric acid in water. To increase the pH, you can add a base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH), until the desired pH level is reached. To decrease the pH, you can add a strong acid, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4), until the desired pH level is achieved.
Natural pH Adjusters for Boric Acid in Water
In terms of home remedies or alternative solutions, DIY users can consider using natural pH adjusters such as:
- Lemon Juice (Citric Acid): Lemon juice can be used to lower the pH of boric acid in water.
- Baking Soda (Sodium Bicarbonate): Baking soda can be used to increase the pH of boric acid in water.
It’s important to monitor the pH level regularly to ensure it remains within the desired range when using these natural pH adjusters.
Importance of pH Control for Boric Acid in Water
When it comes to contaminants or substances present in boric acid in water, it’s essential to consider the pH level. For instance, at seawater pH (8.2), boron mostly presents in boric acid (H3BO3) form. However, the rejection of nonionized boric acid by reverse osmosis (RO) is low due to its smaller size and lack of charge. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor and control the pH level to ensure effective removal of contaminants.
Applications Requiring pH Control of Boric Acid in Water
- Swimming Pools: Boric acid can be used as a pH buffer in swimming pools, and maintaining the proper pH level is crucial for the effectiveness of the buffer system.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems: In RO systems, controlling the pH of boric acid in water is essential for effective removal of contaminants.
- Industrial and Agricultural Uses: Boric acid is used in various industrial and agricultural applications, and the pH level must be carefully monitored and adjusted to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the pH of boric acid in water is crucial for DIY users who want to balance its pH level for various applications. By monitoring and controlling the pH level, users can ensure effective removal of contaminants and maintain the desired pH range for various uses.
References:
– Boric Acid Information
– Boric Acid Technical Fact Sheet
– Boric Acid on Wikipedia
– Boric Acid on PubChem
– Boric Acid in Chemical Engineering