The pH of battery water, a solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and water (H2O), is typically around 0.8 at a 4-5 mol/L concentration, making it a strong acid with a pH value far below the neutral point of 7. This acidity plays a crucial role in the performance, lifespan, and safety of batteries, making it a critical factor for DIY users and professionals alike.
Understanding the Importance of pH in Battery Water
The pH value of battery water is a measure of its acidity, which directly impacts the chemical reactions and overall functionality of the battery. A low pH, such as the 0.8 found in battery water, indicates a highly acidic solution. This acidity is essential for the battery’s ability to store and release electrical energy, as it allows the sulfuric acid to participate in the electrochemical reactions that power the battery.
However, maintaining the proper pH balance is crucial, as deviations from the optimal range can lead to various issues, including:
-
Reduced Battery Performance: If the pH of the battery water becomes too low or too high, it can disrupt the chemical reactions within the battery, leading to a decrease in its ability to store and release energy effectively.
-
Shortened Battery Lifespan: Improper pH levels can accelerate the degradation of the battery’s internal components, such as the plates and separators, reducing the overall lifespan of the battery.
-
Safety Concerns: Highly acidic battery water can pose significant safety risks, as it can be corrosive and potentially harmful if mishandled or spilled.
Maintaining the Proper pH in Battery Water
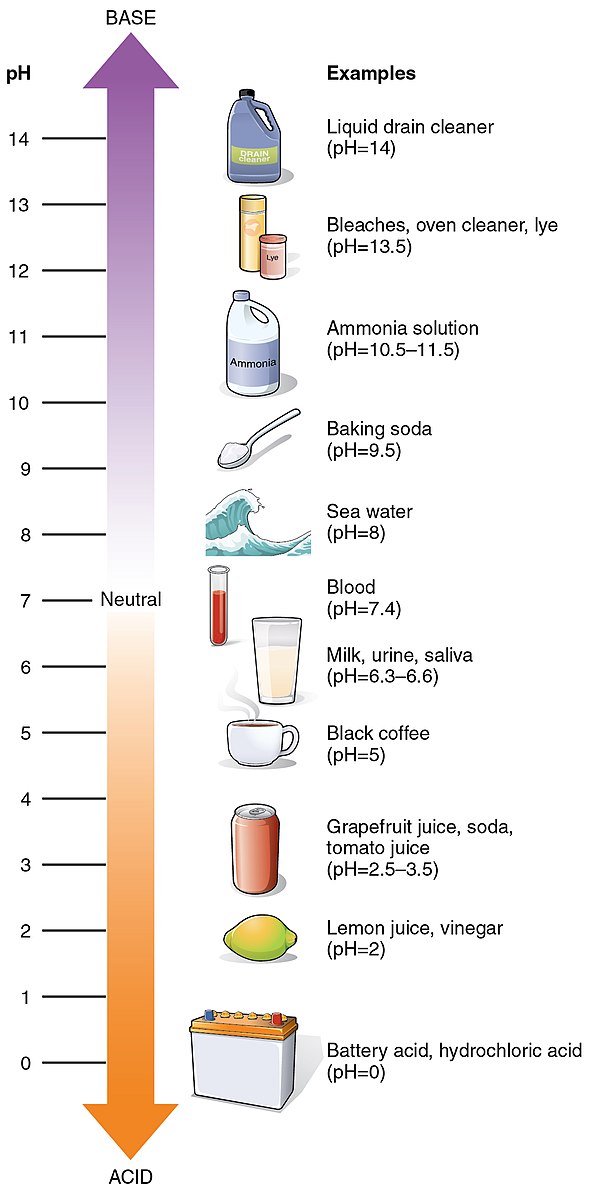 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your battery, it’s essential to maintain the proper pH level in the battery water. Here are some key considerations:
Distilled Water vs. Tap Water
When adding water to a battery, it’s crucial to use distilled water rather than tap water. Tap water may contain various minerals and contaminants that can react with the battery’s chemicals, altering the pH balance and potentially causing damage.
Monitoring and Adjusting pH Levels
Regularly checking the pH level of the battery water and making adjustments as needed is crucial. This can be done using a pH meter or test strips specifically designed for battery applications. If the pH level is too low, you may need to add a small amount of baking soda or other pH-raising agent to bring it back into the optimal range.
Safety Precautions
When handling battery water, it’s essential to take proper safety precautions. Wear protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, and work in a well-ventilated area. Avoid spilling or splashing the acidic solution, as it can be corrosive and harmful if it comes into contact with skin or eyes.
The Dangers of Overwatering and Underwatering
Maintaining the proper electrolyte level in the battery is also crucial for maintaining the optimal pH. Overwatering can cause the battery to bubble over and spill the electrolyte solution, while underwatering can lead to a concentration of the sulfuric acid, further lowering the pH.
To ensure the correct electrolyte level, follow these guidelines:
- The electrolyte level should be 1/8″ above the plates or about ¾” below the top of the cell.
- If the electrolyte level is too low, add distilled water until it reaches the proper level.
- If the electrolyte level is too high, you may need to have a battery professional remove some of the excess solution.
Contaminants and Their Impact on Battery Water pH
In addition to the pH level, it’s important to be aware of potential contaminants that can affect the battery water. These include:
-
Minerals in Tap Water: Minerals found in tap water, such as calcium and magnesium, can react with the battery’s chemicals and convert them into non-rechargeable ions, reducing the battery’s performance.
-
Other Substances: Certain substances, such as oil, grease, or dirt, can also contaminate the battery water and disrupt the chemical balance, leading to decreased efficiency and potential damage.
To mitigate these issues, it’s essential to use only distilled water and keep the battery and its components clean and well-maintained.
Conclusion
The pH of battery water is a critical factor in the performance, lifespan, and safety of batteries. Proper maintenance and safety measures, such as using distilled water, monitoring and adjusting pH levels, and following safety guidelines, can enhance the efficiency and reliability of batteries, making them a cornerstone for numerous modern applications.
References:
– What Is Battery Acid? | The Chemistry Blog – Buy Chemicals Online https://www.chemicals.co.uk/blog/what-is-battery-acid
– Adding Water to a Battery: Everything You Need to Know https://www.foxtronpowersolutions.com/adding-water-to-battery/
– What is the pH of battery acid? – Homework.Study.com https://homework.study.com/explanation/what-is-the-ph-of-battery-acid.html
– What Is Battery Acid? Sulfuric Acid Facts – ThoughtCo https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-battery-acid-603998
– Battery Acid PH Level: Understanding the Basics – Polinovel https://www.polinovelgroup.com/battery-acid-ph-level/
