Zinc carbonate, a white solid compound with the chemical formula ZnCO3, is known for its insolubility in water. This article delves into the pH of zinc carbonate in water, exploring its properties, behavior, and applications.
Understanding Zinc Carbonate
Zinc carbonate is a naturally occurring mineral known as smithsonite. It can also be synthesized by treating cold solutions of zinc sulfate with potassium bicarbonate. The structure of zinc carbonate is similar to that of calcium carbonate, with zinc atoms arranged in an octahedral pattern and each carbonate ion forming bonds with six zinc centers, resulting in three-coordinate oxygen atoms.
The pH of Zinc Carbonate in Water
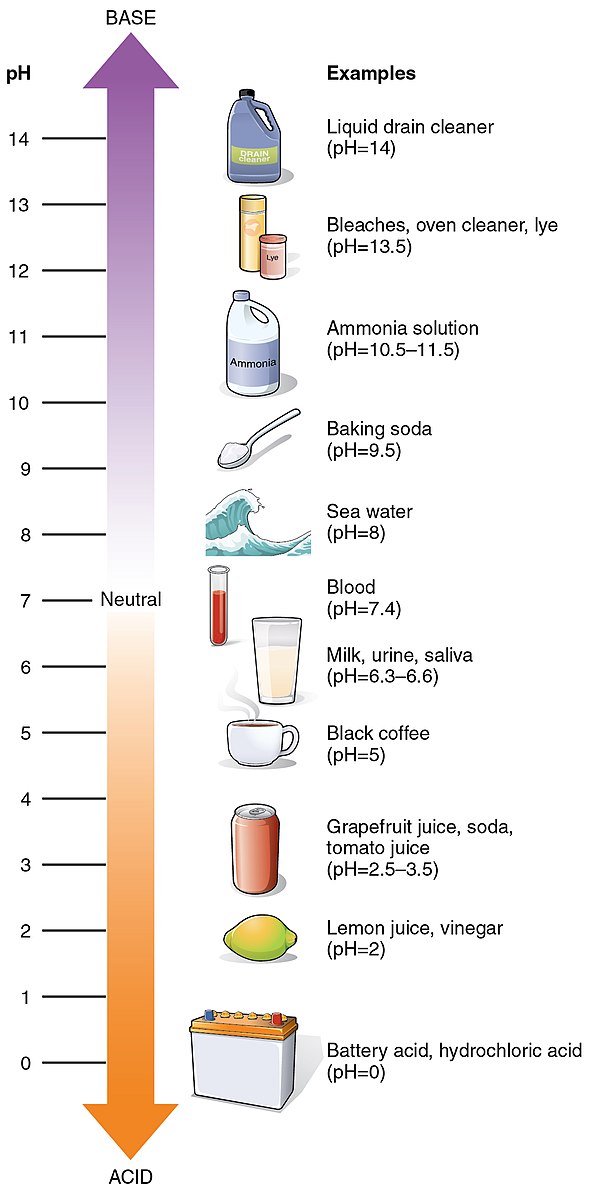 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
Zinc carbonate is insoluble in water, meaning it does not readily dissolve in aqueous solutions. This insolubility is a key factor in determining the pH of zinc carbonate in water.
Solubility and pH
When zinc carbonate is added to water, it does not significantly affect the pH of the solution. This is because the compound is insoluble and does not release any significant amount of hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-) into the water.
Reaction with Acids and Bases
However, zinc carbonate can react with acids and bases, which can impact the pH of the solution. When zinc carbonate reacts with acids, it produces zinc chloride and releases carbon dioxide gas, as shown in the following equation:
ZnCO3 + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + CO2 + H2O
In this reaction, the release of carbon dioxide gas can temporarily lower the pH of the solution, making it more acidic.
On the other hand, when zinc carbonate reacts with bases, it dissolves, forming the hydroxide, which partially dissolves, forming a zincate ion. This reaction can increase the pH of the solution, making it more basic.
ZnCO3 + 2NaOH → Na2[Zn(OH)4]
pH Range
The pH of a solution containing zinc carbonate can vary depending on the specific conditions, such as the presence of other substances and the concentration of the solution. In general, the pH of a solution with zinc carbonate is expected to be close to neutral, around pH 7, due to the insoluble nature of the compound.
Applications and Considerations
Zinc carbonate has various applications, including:
- Sulfur Absorber: Zinc carbonate is used as a sulfur absorber in industrial processes.
- Medicinal Uses: Due to its antiseptic properties, zinc carbonate is used in medications as an astringent and absorbent for the treatment of irritated areas.
- Cosmetic Products: Zinc carbonate is used in the production of creams and ointments, and it has been used in toothpaste to recover dentin in teeth that have been whitened.
When handling or using zinc carbonate, it is important to consider the following:
- Zinc carbonate is not flammable and does not emit toxic fumes when heated.
- It is slightly soluble in ammonia and soluble in dilute acids, alkalis, and ammonium salt solutions.
- Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) should be used when working with zinc carbonate to avoid skin and eye irritation.
Conclusion
In summary, the pH of zinc carbonate in water is generally neutral, around pH 7, due to the insoluble nature of the compound. While zinc carbonate does not significantly affect the pH of water, it can react with acids and bases, which can impact the pH of the solution. Understanding the pH behavior of zinc carbonate is crucial for its various applications in industry, medicine, and cosmetics.
