The pH of potassium iodide (KI) in water is neutral or slightly alkaline, ranging from 7 to 9. This pH range is due to the dissociation of KI in water, which forms K+ and I- ions. The pH of the solution is not affected by the concentration of KI.
Understanding the pH of Potassium Iodide in Water
Potassium iodide is a salt that readily dissolves in water, forming a solution. When KI is dissolved in water, it dissociates into potassium (K+) and iodide (I-) ions. The presence of these ions in the solution determines the pH of the resulting mixture.
The pH of a solution is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution. In the case of KI in water, the pH is not directly affected by the concentration of KI, but rather by the balance of the K+ and I- ions.
The dissociation of KI in water can be represented by the following equation:
KI → K+ + I-
The K+ ions do not significantly affect the pH of the solution, as they are a neutral species. However, the I- ions can undergo a slight hydrolysis reaction, which produces a small amount of hydroxide (OH-) ions. This reaction can be represented as follows:
I- + H2O ⇌ HI + OH-
The presence of the OH- ions in the solution results in a slightly alkaline pH, typically ranging from 7 to 9.
Applications of Potassium Iodide
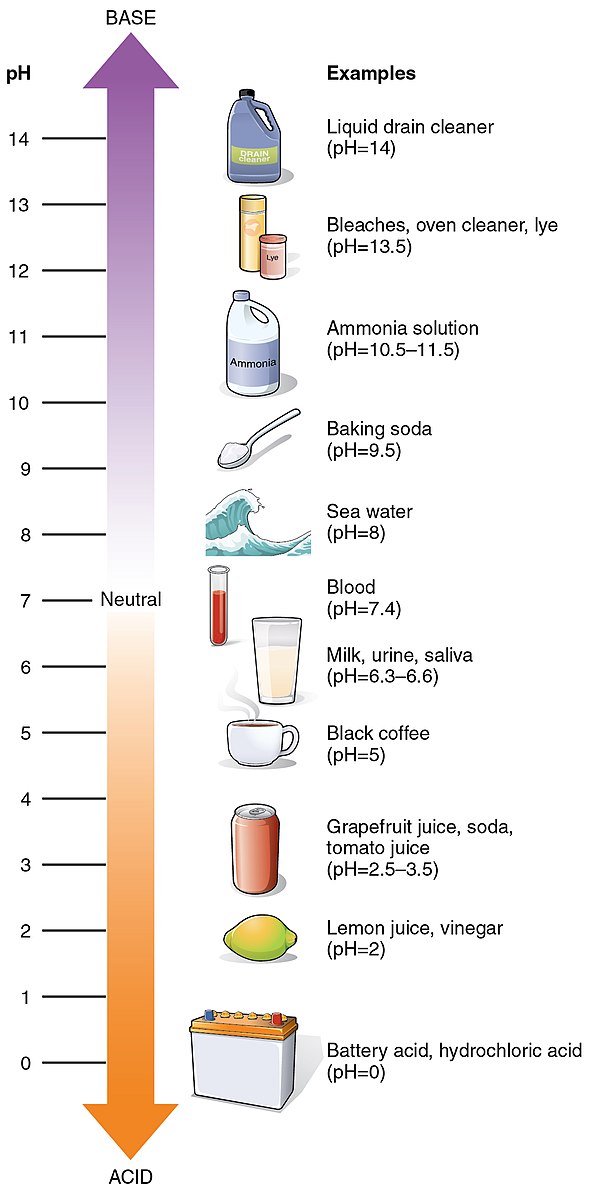 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
Potassium iodide has a wide range of applications, including:
-
Treatment of Radiation Poisoning: KI is used in the treatment of radiation poisoning resulting from a nuclear accident. It helps to block the uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland, reducing the risk of thyroid cancer.
-
Photographic Emulsions: KI is used in the manufacture of photographic emulsions, where it helps to control the sensitivity and contrast of the film.
-
Animal and Poultry Feeds: KI is added to animal and poultry feeds as a source of iodine, which is essential for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
-
Table Salt: KI is often added to table salt as a source of iodine, which is necessary for human health.
-
Analytical Chemistry: KI is used in various analytical chemistry techniques, such as titrations and colorimetric analyses.
Preparing a Saturated Solution of Potassium Iodide
To prepare a saturated solution of potassium iodide in water, the following steps can be followed:
- Weigh out 30 grams of potassium iodide.
- Add 21 milliliters of water to a container.
- Slowly add the 30 grams of KI to the water, stirring constantly to ensure complete dissolution.
- The resulting solution will be 30 milliliters in volume and will have a slightly alkaline pH, ranging from 7 to 9.
It is important to note that the pH of the KI solution is not affected by the concentration of the salt, as long as the solution remains saturated.
Compatibility and Handling of Potassium Iodide Solutions
When handling and storing potassium iodide solutions, it is important to be aware of the following compatibility and safety considerations:
-
Incompatible Substances: KI is incompatible with alkaloidal salts, chloral hydrate, tartaric and other acids, calomel, potassium chlorate, and metallic salts. These substances should be kept away from KI solutions.
-
Oxidation: KI solutions can be susceptible to oxidation, which can affect the concentration and pH of the solution. To prevent oxidation, it is recommended to add a small amount of alkali to the solution to maintain a slightly alkaline pH.
-
Dosage and Consumption: When consuming KI as a dietary supplement, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a healthcare professional for the appropriate dosage. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a daily iodine intake of 150 micrograms for adults, which can be obtained through dietary sources or supplements.
Conclusion
In summary, the pH of potassium iodide in water is neutral or slightly alkaline, ranging from 7 to 9. This pH range is due to the dissociation of KI in water, which forms K+ and I- ions. The pH of the solution is not affected by the concentration of KI.
Potassium iodide has a wide range of applications, including the treatment of radiation poisoning, the manufacture of photographic emulsions, and use in animal and poultry feeds, table salt, and analytical chemistry. When preparing a saturated solution of KI in water, it is important to follow the appropriate steps and be aware of the compatibility and handling considerations.
References:
– What is the pH of .20 M Potassium Iodide (KI)? – Homework.Study.com
– Potassium iodide – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
– Potassium Iodide 2 mol/l (2M) (pH 7.0) volumetric solution
– Potassium Iodide – DrugFuture
– Potassium Iodide | KI | CID 4875 – PubChem
– Iodine Deficiency Disorders – World Health Organization (WHO)
