Potassium carbonate (K2CO3) is a white salt that is soluble in water and forms a strongly alkaline solution with a pH of around 11.6. When dissolved in water, potassium carbonate dissociates completely to produce potassium cations (K+) and carbonate anions (CO3 2-), which can react with water to form bicarbonate anions (HCO3-) and hydroxide ions (OH-), further increasing the pH of the solution.
Understanding the pH of Potassium Carbonate in Water
The pH of a solution of potassium carbonate in water can be calculated using the pKa values of carbonic acid and the reaction equilibrium constants. For example, a solution of K2CO3 with a pH of 11.90 would have a concentration of around 0.025 M.
Factors Affecting the pH of Potassium Carbonate in Water
- Concentration of Potassium Carbonate: The higher the concentration of potassium carbonate in the water, the higher the pH of the solution.
- Presence of Impurities: Any acidic impurities in the water or in the potassium carbonate itself can react with the potassium hydroxide (KOH) formed during the dissolution of potassium carbonate, forming new substances and affecting the pH.
- Temperature: The pH of a potassium carbonate solution can also be affected by temperature, with higher temperatures generally leading to a higher pH.
Applications of Potassium Carbonate in Water
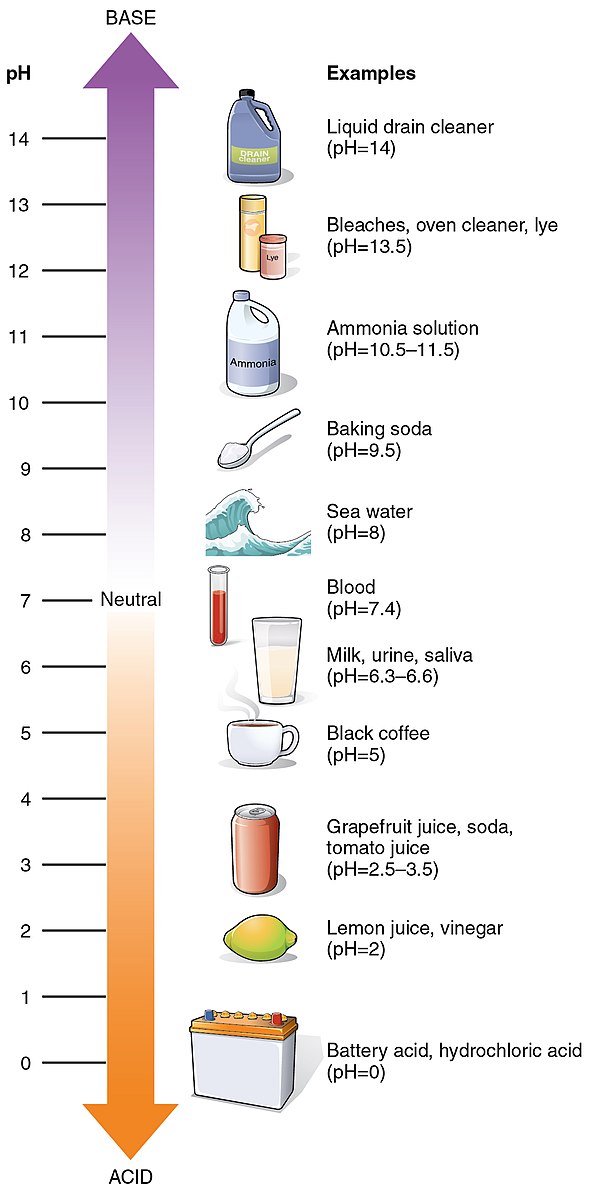 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and glass, but it also has many other applications, such as:
- Mild Drying Agent: Potassium carbonate can be used as a mild drying agent in various applications.
- Buffering Agent: Potassium carbonate can be used as a buffering agent in the production of mead or wine, helping to maintain the desired pH.
- Acidity Regulator: Potassium carbonate can be used as an acidity regulator in Swedish snus snuff tobacco.
Dealing with Impurities in Potassium Carbonate Solutions
To deal with any impurities in a potassium carbonate solution, it is important to:
- Use High-Purity Potassium Carbonate: Ensure that the potassium carbonate used is of high purity to minimize the presence of any acidic impurities.
- Test the Water: Test the water for acidity before using it to make a potassium carbonate solution.
- Neutralize Acidic Impurities: If the water is acidic, it can be treated with a base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH), to raise the pH and neutralize any acidic impurities.
- Recrystallize Potassium Carbonate: Alternatively, the potassium carbonate can be recrystallized from water to remove any impurities.
Conclusion
Potassium carbonate is a strongly alkaline compound with a pH of around 11.6 when dissolved in water. It has a wide range of applications, including in the production of soap and glass, as a mild drying agent, a buffering agent, and an acidity regulator. When using potassium carbonate in water, it is important to consider the presence of any acidic impurities and take appropriate measures to ensure the purity of the solution.
References:
– Byju’s. (n.d.). Potassium Carbonate – Structure, Properties & Uses of K2CO3. Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://byjus.com/chemistry/potassium-carbonate/
– PubChem. (n.d.). Potassium Carbonate | K2CO3 | CID 11430. Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Potassium-Carbonate
– Socratic. (2017, April 9). What is the concentration of a solution of K2CO3 that has pH = 11.90? Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://socratic.org/questions/what-is-the-concentration-of-a-solution-of-k-2co-3-that-has-ph-11-90
– Wikipedia. (n.d.). Potassium carbonate. Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassium_carbonate
– UK Aquatic Plant Society. (2022, January 13). Potassium Carbonate (K2CO3) vs pH. Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://www.ukaps.org/forum/threads/potassium-carbonate-k2co3-vs-ph.67950/
– YouTube. (2020, May 2). Is K2CO3 acidic, basic, or neutral (dissolved in water)? Retrieved April 27, 2024, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x1RV9Ho2G7g
