The pH value of phosphate water can range from acidic (low pH) to basic (high pH), but the optimal pH range for most aquatic systems, including aquaponics, is between 5.5 and 7.2. This range ensures optimal availability and uptake of phosphorus (P) by plants. Understanding the impact of pH on phosphate water is crucial for maintaining a healthy and thriving aquatic ecosystem.
Understanding Phosphate Water pH
Phosphate water, which contains dissolved phosphate ions, can have varying pH levels depending on the presence of other contaminants or substances. In aquaponics systems, the main ions in the nutrient solution can influence the chemical composition and availability of nutrients, including phosphorus. In freshwater systems, pH is believed to be an important regulating factor for the release of phosphate from sediments.
Optimal pH Range for Phosphate Water
The optimal pH range for phosphate water is between 5.5 and 7.2. At this range, phosphate ions are readily available in the solution, allowing for optimal uptake by plants. When the pH falls below 5.5, phosphate ions become more soluble, but they may also bind to other cations, forming insoluble compounds that are less available to plants. Conversely, when the pH rises above 7.2, phosphate tends to bind to cations, forming insoluble species, which can lead to a decrease in free phosphate ions available in the solution.
Balancing pH in Phosphate Water
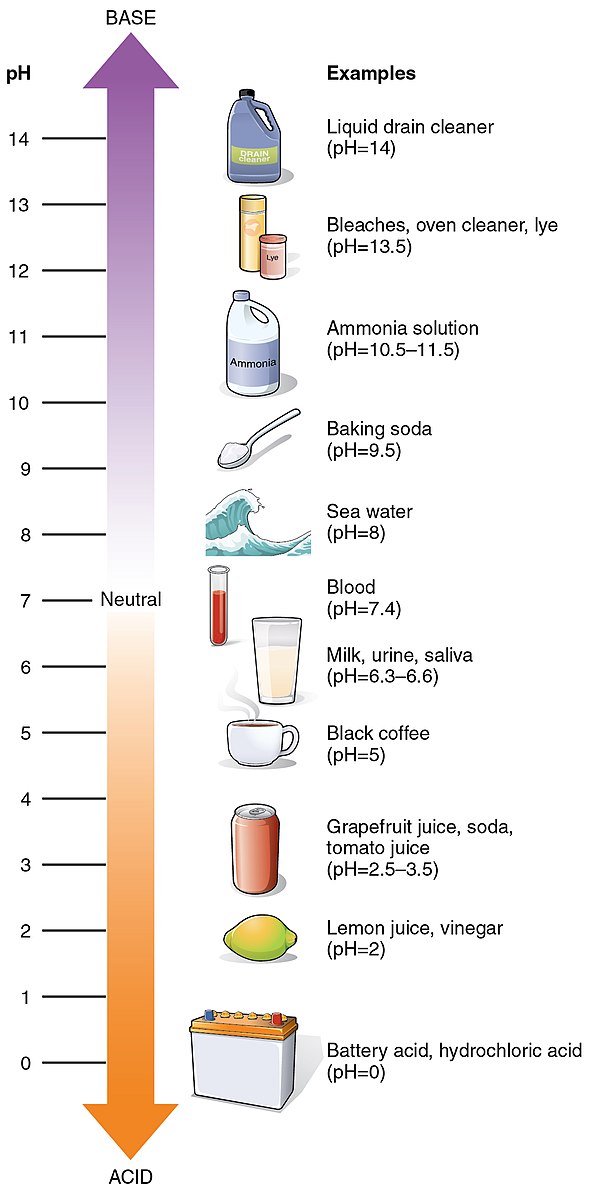 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
To maintain the optimal pH range in phosphate water, various methods can be employed, depending on the specific system and requirements.
Aquaponics Systems
In aquaponics systems, maintaining the pH within the recommended range of 5.5-7.2 is crucial for optimal phosphorus availability and uptake by plants. This can be achieved through the addition of pH adjusters, such as acid or base, to the system. Regular monitoring of pH levels is also essential to ensure that the system remains within the optimal range.
Home Remedies for pH Balancing
Home remedies for balancing pH in phosphate water can include the use of natural pH adjusters, such as lemon juice or vinegar for lowering pH, and baking soda for raising pH. However, it is important to use these remedies with caution, as excessive additions can lead to rapid pH changes, which can be harmful to aquatic life.
Factors Affecting Phosphate Water pH
Several factors can influence the pH of phosphate water, including the presence of contaminants or other substances.
Aquaponics Nutrient Solution
In aquaponics systems, the main ions in the nutrient solution can affect the chemical composition and availability of nutrients, including phosphorus. The pH of the nutrient solution can be influenced by the balance of these ions, which may require adjustments to maintain the optimal pH range.
Freshwater Systems
In freshwater systems, pH is believed to be an important regulating factor for the release of phosphate from sediments. Changes in pH can affect the solubility and availability of phosphate, which can impact the overall ecosystem.
Monitoring and Maintaining Optimal pH
Regular monitoring and careful adjustment of pH levels are essential for maintaining a healthy and thriving aquatic system, including aquaponics.
Monitoring pH Levels
Regularly testing the pH of phosphate water is crucial to ensure that it remains within the optimal range of 5.5-7.2. This can be done using pH meters, test kits, or other reliable methods.
pH Adjustment Strategies
If the pH of phosphate water falls outside the optimal range, adjustments can be made using pH adjusters, such as acids or bases. It is important to make these adjustments gradually and carefully to avoid rapid pH changes that can be harmful to aquatic life.
Conclusion
The pH of phosphate water plays a crucial role in the availability and uptake of phosphorus by plants and other aquatic organisms. Maintaining the optimal pH range of 5.5-7.2 is essential for ensuring a healthy and thriving aquatic ecosystem. By understanding the factors that affect phosphate water pH and implementing appropriate balancing strategies, aquaponics and freshwater systems can be managed effectively to support the growth and development of aquatic life.
References:
– Reef2Reef – pH Effect on Phosphate
– Science Direct – The effect of pH on phosphate adsorption by hydrous ferric oxide
– Indiana Department of Environmental Management – Volunteer Stream Monitoring Manual
– PubMed – Phosphate adsorption on aluminum oxide influenced by pH and natural organic matter
– ACS Earth and Space Chemistry – Phosphate Adsorption on Iron Oxides: Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations
