The pH of lactic acid in water is around 3.5, which is slightly acidic. This is because lactic acid is a weak acid, meaning it only partially dissociates in water to form lactate and H+ ions. The pH of lactic acid in water can vary depending on the concentration of lactic acid, and contaminants or chemicals can also affect the pH.
Understanding the Chemistry of Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C₃H₆O₃. It is a weak acid, meaning it only partially dissociates in water to form lactate and hydrogen ions (H+). The degree of dissociation is determined by the acid’s pKa value, which for lactic acid is 3.86.
At a pH of 3.86, 50% of the lactic acid molecules are dissociated, and the remaining 50% are in the undissociated form. As the pH decreases below 3.86, the concentration of H+ ions increases, and more lactic acid molecules become dissociated. Conversely, as the pH increases above 3.86, the concentration of H+ ions decreases, and more lactic acid molecules remain in the undissociated form.
Factors Affecting the pH of Lactic Acid in Water
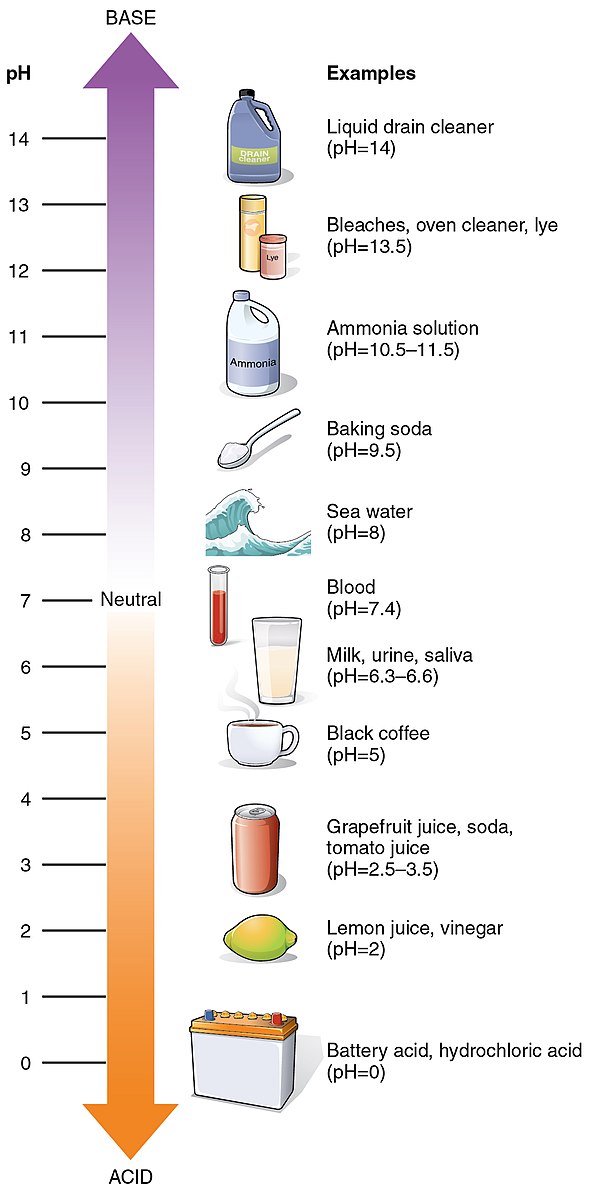 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
The pH of lactic acid in water can be influenced by several factors:
-
Concentration of Lactic Acid: The higher the concentration of lactic acid, the lower the pH of the solution. For example, a 5% lactic acid solution in water has a pH of around 1.9, while a 10% lactic acid solution in water has a pH of around 2.5.
-
Presence of Contaminants or Chemicals: Other acids or bases, such as hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide, can alter the pH of the lactic acid solution by adding or removing H+ ions.
-
Temperature: The pH of lactic acid in water can also be affected by temperature, as the degree of dissociation of the acid can change with temperature.
Balancing the pH of Lactic Acid in Water
To maintain the desired pH range for various applications, it is important to understand the chemical properties of lactic acid and how to adjust the pH as needed.
Using pH Adjusters
If the pH of the lactic acid solution is too low (too acidic), it can be increased by adding a base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). Conversely, if the pH is too high (too basic), it can be decreased by adding an acid, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
It is important to add the pH adjusters slowly and carefully, as adding too much can cause the solution to become too basic or too acidic.
Home Remedies
For minor pH adjustments, a simple home remedy is to add baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO₃) to the lactic acid solution. The baking soda will react with the excess H+ ions, neutralizing the acidity and raising the pH.
However, it is important to add the baking soda slowly and carefully, as adding too much can cause the solution to become too basic.
Conclusion
The pH of lactic acid in water is typically around 3.5, but it can vary depending on the concentration of lactic acid and the presence of other substances. To maintain the desired pH range, it is important to understand the chemical properties of lactic acid and to use pH adjusters or home remedies as needed.
By carefully monitoring and adjusting the pH of lactic acid in water, you can ensure that it is suitable for various applications, such as in the cosmetic, food, or pharmaceutical industries.
References:
- What is the pH of lactic acid? – Quora. Available at: https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-pH-of-lactic-acid
- Lactic acid and lactate. Available at: https://lactic-acid.com/lactic-acid-and-lactate/
- Lactic Acid | HC3H5O3 | CID 612 – PubChem. Available at: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lactic-Acid
- What should be the pH of 5% lactic in water? – Chemists Corner. Available at: https://chemistscorner.com/cosmeticsciencetalk/discussion/what-should-be-the-ph-of-5-lactic-in-water/
- Lactic acid – Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactic_acid
- Find the pH of 41.5 g lactic acid in 500 mL solution – YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nF1GwrcmYxI
