The pH of dehumidifier water can range from 5.7 to 7.8, depending on the specific model and environmental conditions. This water, produced through the condensation of moisture from the air, may contain trace amounts of contaminants that can affect its pH and suitability for various applications, including gardening.
Understanding the pH Range of Dehumidifier Water
Dehumidifier water can have a pH range of 5.7 to 7.8, which is slightly acidic to neutral. This variation in pH can be attributed to several factors, including the composition of the air, the materials used in the dehumidifier, and the presence of any dissolved minerals or contaminants.
Factors Affecting the pH of Dehumidifier Water
-
Air Composition: The pH of dehumidifier water can be influenced by the composition of the air being processed. If the air contains higher levels of carbon dioxide or other acidic compounds, the resulting water may have a lower pH.
-
Dehumidifier Materials: The materials used in the construction of the dehumidifier, such as the coils or the tank, can also contribute to the pH of the water. Some materials may release ions that can affect the water’s pH.
-
Dissolved Contaminants: Trace amounts of metals, minerals, or other contaminants present in the air can dissolve into the dehumidifier water, altering its pH and potentially introducing other issues.
Implications for Gardening and Other Applications
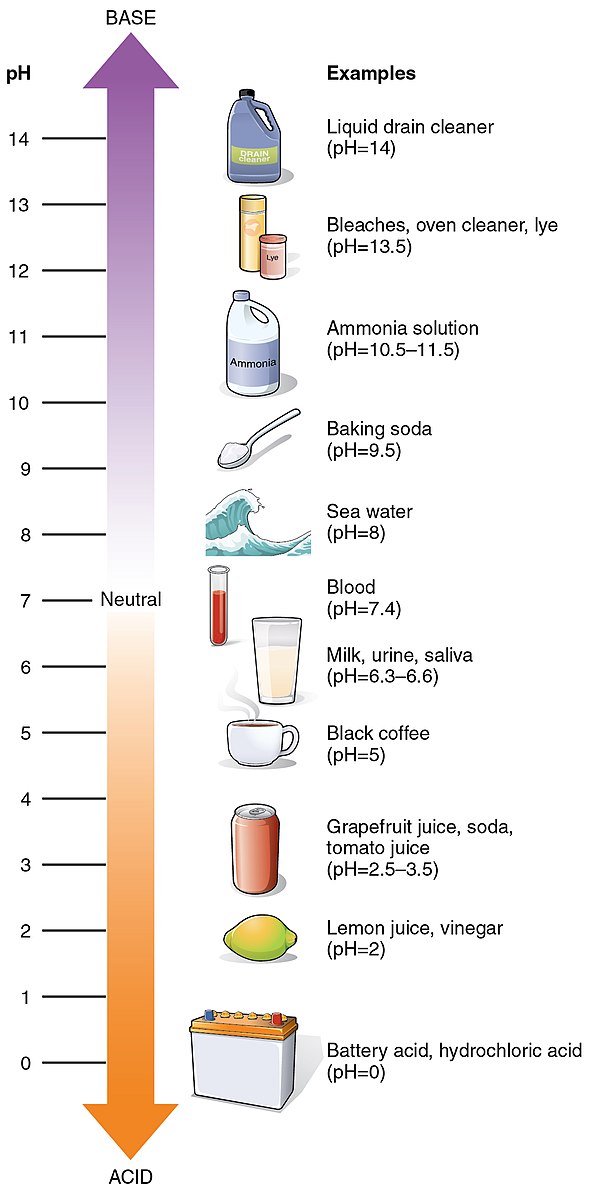 Image source: OpenStax College
Image source: OpenStax College
When using dehumidifier water for gardening or other applications, it is essential to consider the pH and potential contaminants present in the water.
Gardening Considerations
-
pH Stability: The pH of dehumidifier water may not be stable, and it can fluctuate over time. This can lead to issues with nutrient uptake and plant health, as plants have specific pH preferences for optimal growth.
-
Nutrient Availability: The presence of contaminants or metals in the dehumidifier water can interfere with the availability of essential nutrients for plants, leading to nutrient lockout or toxicity.
-
Microbial Concerns: Dehumidifier water may contain trace amounts of bacteria or other microorganisms, which can potentially harm plants or introduce other issues if not properly addressed.
To mitigate these concerns, it is recommended to regularly test the pH of the dehumidifier water and adjust it as needed using pH-adjusting solutions or by mixing it with other water sources. Additionally, it is crucial to maintain the dehumidifier and its components to minimize the buildup of contaminants.
Other Applications
Dehumidifier water may also be used for various other purposes, such as:
-
Household Cleaning: The pH and potential contaminants in dehumidifier water may affect its suitability for cleaning tasks, as it may not be as effective or may leave residues.
-
Aquarium Topping-Up: The pH and water quality of dehumidifier water should be carefully evaluated before using it to top up aquarium water, as it may not be compatible with the specific requirements of the aquatic ecosystem.
-
Humidifier Refilling: When using dehumidifier water to refill a humidifier, it is essential to ensure the pH and water quality are within the recommended ranges to prevent any issues with the humidifier’s operation or the indoor air quality.
Ensuring Safe and Effective Use of Dehumidifier Water
To ensure the safe and effective use of dehumidifier water, it is recommended to take the following steps:
-
Regular Testing: Regularly test the pH and, if possible, the presence of contaminants in the dehumidifier water to ensure it meets the requirements for your intended use.
-
pH Adjustment: If the pH of the dehumidifier water is not within the desired range, use pH-adjusting solutions or mix it with other water sources to achieve the optimal pH.
-
Dehumidifier Maintenance: Regularly clean and maintain the dehumidifier to minimize the buildup of contaminants in the water.
-
Additional Precautions: Consider boiling the dehumidifier water or using other sterilization methods to kill any potential bacteria or microorganisms, especially if the water is intended for use in sensitive applications like gardening or aquarium maintenance.
By understanding the pH range of dehumidifier water and taking the necessary precautions, you can ensure its safe and effective use in a variety of applications, including gardening, household cleaning, and more.
