The pH of rabbit urine is typically alkaline, ranging from 7.5 to 9, due to their herbivorous diet and high mineral concentration. This pH range is considered normal and indicates a healthy acid-base balance in rabbits. Understanding the factors that affect urine pH and recognizing potential health issues can help pet owners maintain their rabbit’s well-being.
Normal pH Range for Rabbit Urine
The normal pH range for rabbit urine is as follows:
| pH Range | Condition |
|---|---|
| pH 8 or more | Typical pH range for rabbits fed a correct diet |
| pH 7.5 to 9 | Also considered normal, indicating a healthy acid-base balance |
Detecting Health Issues through Urine pH
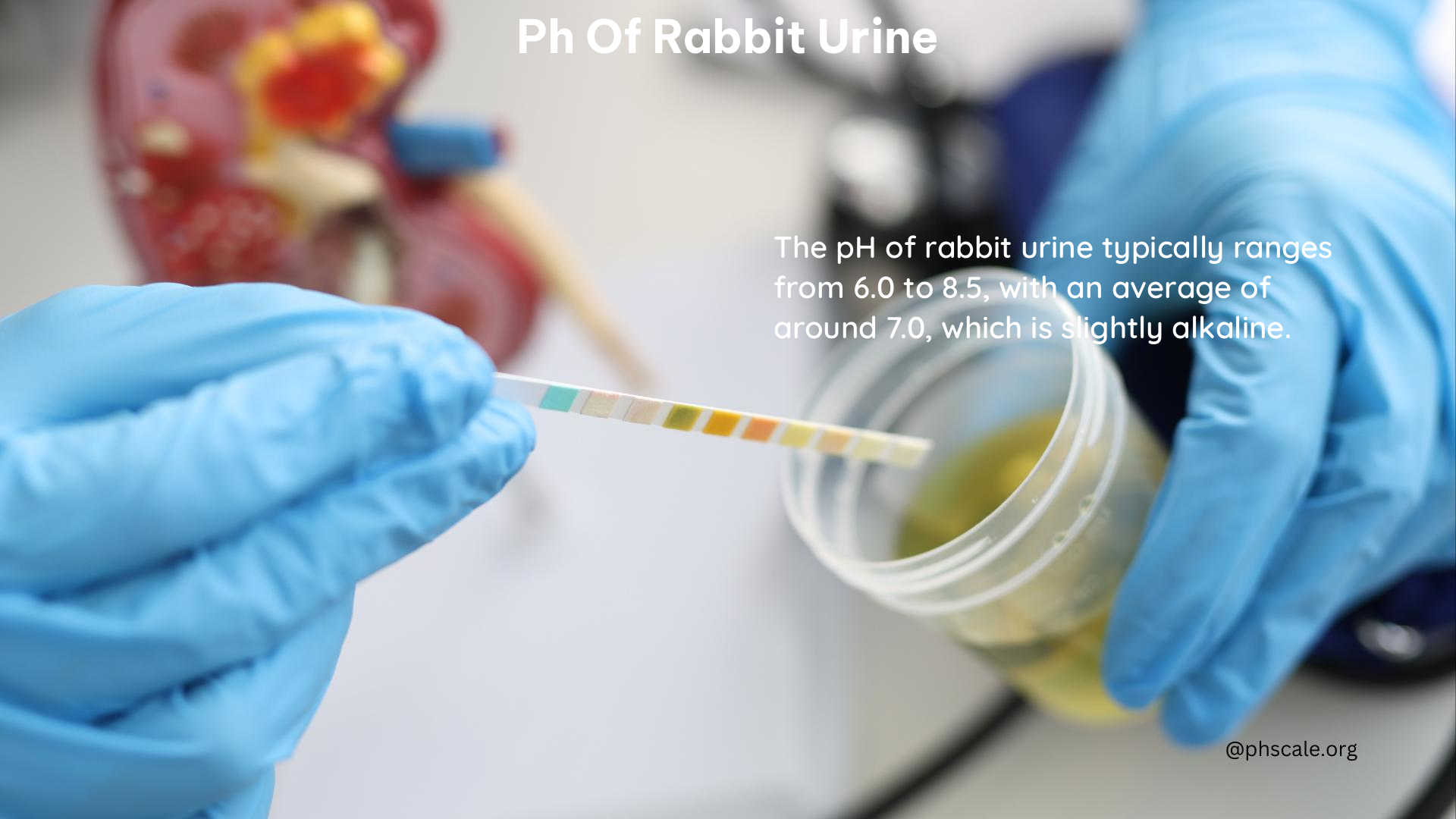
Monitoring the pH of rabbit urine can provide valuable insights into their overall health. Deviations from the normal range may indicate the following:
Acidic Urine (pH < 7.5)
- Indicates acidosis due to conditions such as anorexia, fever, pregnancy toxemia, or hepatic lipidosis.
Neutral or Acidic Urine
- Can be a sign of compromised renal function or other health issues.
Factors Affecting Urine pH
Several factors can influence the pH of rabbit urine, including:
- Diet: A diet with a high cation-anion balance (CAB) can lead to more alkaline urine, while a diet with a low CAB can result in more acidic urine.
- Health Conditions: Certain health issues, such as acidosis or kidney problems, can affect urine pH.
Contaminants and Chemicals in Rabbit Urine
Rabbit urine can contain various contaminants and chemicals, including:
- Minerals: Rabbit urine is rich in minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which can affect pH levels.
- Bacterial Contaminants: Urine samples can be contaminated with bacteria, which can affect pH levels and other test results.
Maintaining a Healthy Urine pH
To maintain a healthy pH balance in rabbit urine, consider the following:
- Provide a Balanced Diet: Ensure your rabbit’s diet includes a mix of hay, vegetables, and limited amounts of pellets to maintain a healthy acid-base balance.
- Monitor Water Intake: Encourage your rabbit to drink plenty of water to help flush out minerals and maintain a healthy urinary system.
- Consult a Veterinarian: If you suspect any health issues or notice changes in your rabbit’s urine pH, consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
By understanding the normal pH range of rabbit urine and the factors that can affect it, pet owners can proactively monitor their rabbit’s health and take appropriate measures to maintain a healthy urinary system.
References
- Avian & Exotics Service. (2023). Rabbit Urinalysis. Retrieved from https://avesvet.com.au/vet-info/f/rabbit-urinalysis
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2007). Rabbit Clinical Pathology. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7185592/
- PubMed. (2017). Effect of cation-anion balance in feed on urine pH in rabbits. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28299839/.
