The pH of urine in females is a crucial indicator of overall health, as it can be influenced by various factors such as diet, medical conditions, and medications. Understanding the normal pH range, factors affecting it, and the potential implications of an imbalanced pH can help women maintain a healthy urinary system.
Normal pH Range
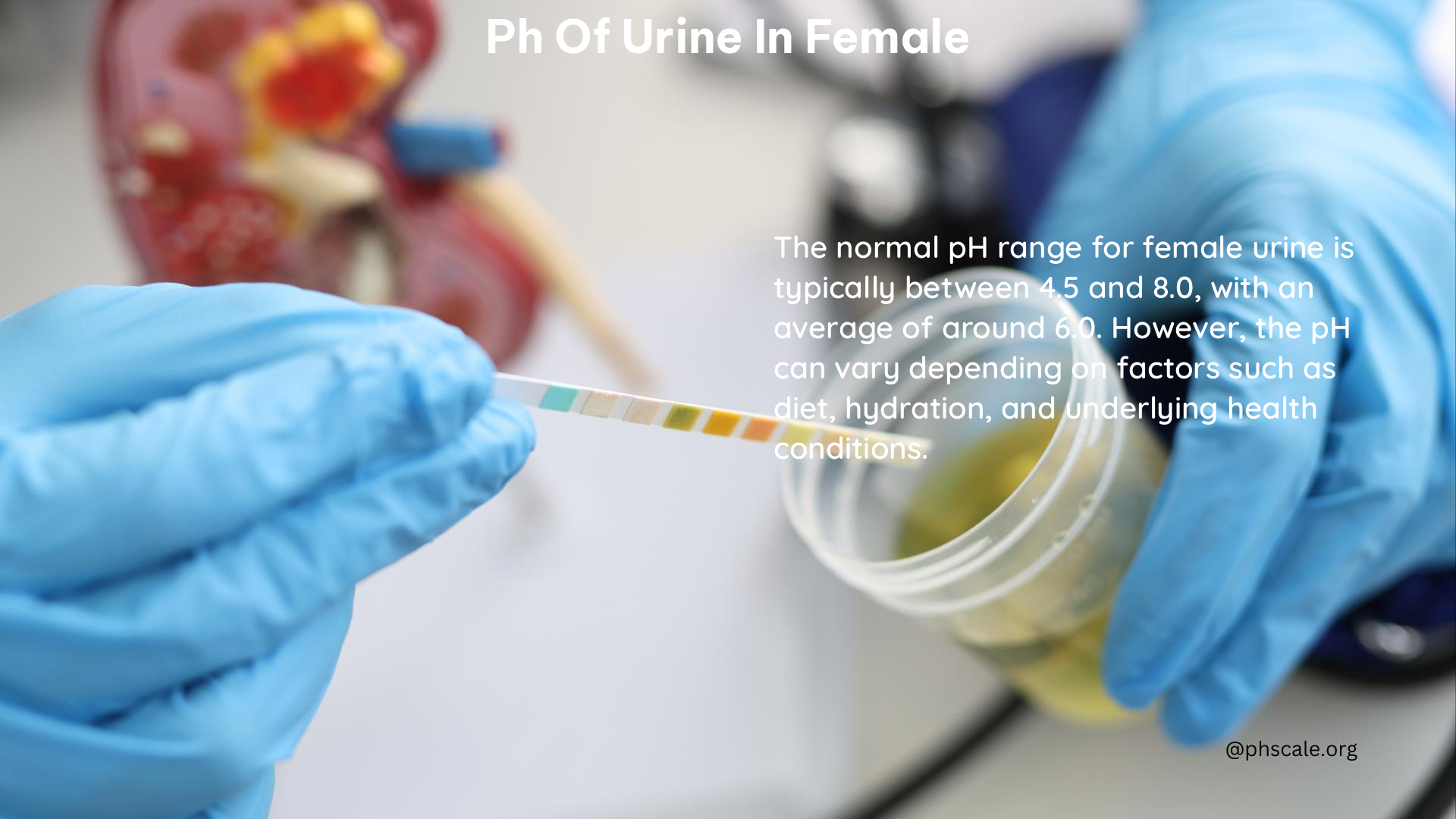
The normal pH range for urine in women is between 4.5 and 8.0, with an average pH of around 6.0. This range is essential for maintaining a healthy urinary tract and preventing the formation of kidney stones or urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Factors Affecting Urine pH
Diet
The food and beverages you consume can significantly impact your urine pH. A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and non-cheese dairy products can increase urine pH, making it more alkaline. Conversely, a diet high in fish, meat products, and cheese can decrease urine pH, making it more acidic.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also affect urine pH levels. These include kidney stones, diabetic ketoacidosis, dehydration, acidosis, and urinary tract infections.
Medications
Some medications, such as acetazolamide, ammonium chloride, methenamine mandelate, potassium citrate, sodium bicarbonate, and thiazide diuretics, can impact urine pH levels.
Imbalanced pH and Urinary Health
An imbalanced urine pH in women can lead to various urinary health issues, including:
- Kidney Stones: A highly acidic or basic environment can increase the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Abnormal pH levels can create an environment conducive to UTIs.
Balancing Urine pH
To maintain a healthy urine pH, consider the following strategies:
Dietary Changes
Adjust your diet to include more alkaline or acidic foods based on your urine pH levels. For example, if your urine is too acidic, you can increase your intake of alkaline foods like fruits and vegetables.
Hydration
Drink plenty of water to help maintain a healthy pH balance.
Medication Management
If possible, avoid medications that can affect urine pH levels.
Home Remedies
Some home remedies that can help balance urine pH include:
- Lemon Juice: Drinking lemon juice can help increase urine pH and make it more alkaline.
- Baking Soda: Consuming baking soda can help neutralize acidic urine.
- Cranberry Juice: Drinking cranberry juice may help prevent UTIs by maintaining a healthy pH balance.
Contaminants and Chemicals
Common contaminants and chemicals that can affect urine pH include:
- Bacteria: Bacterial infections can alter urine pH levels.
- Medication Residues: Certain medications can leave residues in the urine, affecting pH levels.
- Food Additives: Some food additives can alter urine pH levels.
Dealing with Contaminants
To ensure accurate urine pH testing and avoid contamination, follow these steps:
- Clean-Catch Urine Sample: Clean the genital area before urination and collect urine midstream.
- Avoid Contaminating the Sample: Avoid touching the inner portion of the urine collection cup and prevent any contaminants from entering the cup.
- Proper Storage and Handling: Store and handle the urine sample properly to prevent contamination.
Helpful pH Quantities to Consume
To maintain a healthy urine pH, consider the following:
- Alkaline Foods: Include alkaline foods like fruits, vegetables, and non-cheese dairy products in your diet.
- Acidic Foods: If you have acidic urine, consume more acidic foods like fish, meat products, and cheese.
History
The study of urine pH dates back to the 1980s, with research focusing on the regulation of acid-base metabolism and its impact on urine pH.
References
- Mechanism for higher urine pH in normal women compared with men (2018) – This study explores the differences in urine pH between men and women, attributing the higher pH in women to differences in diet and gastrointestinal anion uptake.
- Mechanism for higher urine pH in normal women compared with men (2018) – This study provides detailed information on the regulation of acid-base metabolism and its impact on urine pH, highlighting the role of gastrointestinal anion uptake in women.
- What to Know About a Urine pH Test (2023) – This article provides an overview of urine pH tests, including the normal pH range, factors affecting pH levels, and the importance of the test in diagnosing various medical conditions.
- Urine pH Level Test: Purpose, Procedure, Results & More (2021) – This article discusses the purpose and procedure of urine pH tests, as well as the results and their implications for overall health.
- Urine pH test Information (Mount Sinai) – This resource provides information on the urine pH test, including how it is performed, how to prepare, and why it is done.
