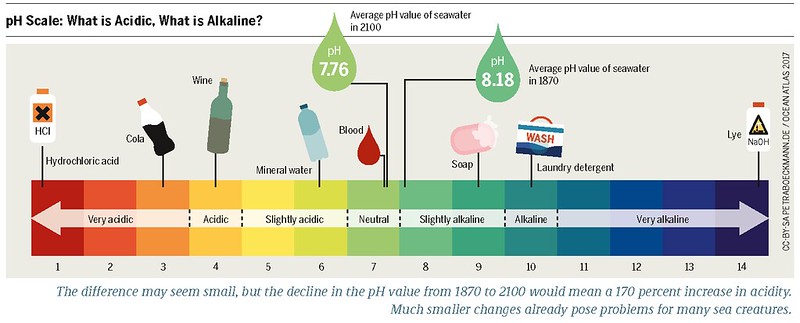
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, with pH values ranging from 0 to 14. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a strong acid with a pH value of approximately 1, making it a highly acidic substance. When HCl is added to water, it dissociates completely into hydrogen ions (H+) and chloride ions (Cl-), leading to an increase in hydrogen ion concentration and a decrease in pH.
Understanding the pH of Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid is a colorless, corrosive liquid that is widely used in various industries, such as chemical manufacturing, metal processing, and water treatment. The pH of a hydrochloric acid solution is directly related to the concentration of HCl, with higher concentrations resulting in lower pH values.
The dissociation of HCl in water can be represented by the following equation:
HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
The hydrogen ions (H+) released during the dissociation process are responsible for the acidic nature of the solution. The pH of the solution can be calculated using the following formula:
pH = -log[H+]
Where [H+] represents the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
For example, a 0.1 M solution of hydrochloric acid would have a pH of approximately 1, as the concentration of hydrogen ions would be 0.1 M. This means that the solution is highly acidic, with a pH value much lower than the neutral pH of 7.
Measuring the pH of Hydrochloric Acid and Water
The pH of a hydrochloric acid and water solution can be measured using a pH meter or pH indicator paper. When measuring the pH, it is important to consider the following factors:
-
Concentration of HCl: The pH of the solution will depend on the concentration of HCl. Higher concentrations of HCl will result in lower pH values.
-
Temperature: The pH of a solution can be affected by temperature. As the temperature increases, the pH of the solution may change slightly.
-
Contamination: Impurities or contaminants in the hydrochloric acid can affect the pH of the solution. For example, the presence of iron ions can lead to the formation of iron(III) chloride, which can increase the pH of the solution.
To ensure accurate pH measurements, it is important to follow proper procedures for sample preparation, calibration of the pH meter, and temperature control.
Safety Considerations
When working with hydrochloric acid, it is essential to take appropriate safety precautions to prevent exposure to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. This includes:
- Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat.
- Working in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling the fumes.
- Properly storing and handling the hydrochloric acid to prevent spills or leaks.
- Immediately rinsing any affected areas with water in case of accidental exposure.
- Seeking medical attention if necessary.
Factors Affecting the pH of Hydrochloric Acid and Water
The pH of a hydrochloric acid and water solution can be influenced by several factors, including:
-
Concentration of HCl: As mentioned earlier, the pH of the solution is directly related to the concentration of HCl. Higher concentrations of HCl will result in lower pH values.
-
Temperature: The pH of the solution can be affected by temperature changes. As the temperature increases, the pH of the solution may change slightly.
-
Impurities and Contaminants: The presence of impurities or contaminants in the hydrochloric acid can affect the pH of the solution. For example, the presence of iron ions can lead to the formation of iron(III) chloride, which can increase the pH of the solution.
-
Dilution: When hydrochloric acid is diluted with water, the pH of the solution will increase, as the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases.
Applications of Hydrochloric Acid and Water Solutions
Hydrochloric acid and water solutions have a wide range of applications, including:
- Industrial Applications: Hydrochloric acid is used in various industrial processes, such as metal cleaning, pickling, and etching.
- Water Treatment: Hydrochloric acid is used in water treatment processes to adjust the pH of the water, making it suitable for various applications.
- Chemical Synthesis: Hydrochloric acid is used as a reagent in various chemical synthesis reactions.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Hydrochloric acid is used in the production of certain pharmaceutical drugs and as a pH adjuster in various formulations.
Conclusion
The pH of hydrochloric acid and water is a crucial factor to consider in various applications, from industrial processes to water treatment and chemical synthesis. Understanding the relationship between the concentration of HCl and the pH of the solution, as well as the factors that can affect the pH, is essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of hydrochloric acid and water solutions.
References:
- Quora. How does the concentration of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in water affect its pH? Retrieved from: https://www.quora.com/How-does-the-concentration-of-hydrochloric-acid-HCl-in-water-affect-its-pH
- Aqion. pH of Common Acids and Bases. Retrieved from: https://www.aqion.de/site/ph-of-common-acids
- Sciencing. What Will Happen to the pH of Water If HCI Is Added? Retrieved from: https://sciencing.com/happen-ph-water-hci-added-9037.html