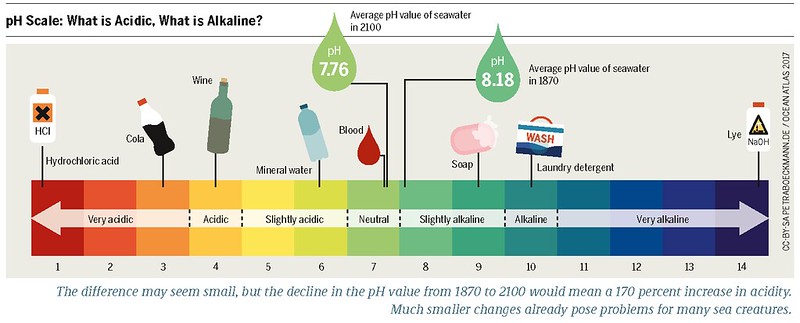
The pH of water from metamorphic rocks can range from less than 1 to 14, with low values being the most acidic and high values being the most alkaline. The pH of most natural waters, including those from metamorphic rocks, lies between 5.5 and 8.5. Understanding the factors that influence the pH of water from metamorphic rocks is crucial for maintaining a healthy environment and ensuring the safety of water resources.
Factors Influencing the pH of Water from Metamorphic Rocks
The pH of water from metamorphic rocks can be influenced by various factors, including the minerals present in the rocks and the surrounding environment.
Mineral Composition
The minerals present in metamorphic rocks can significantly impact the pH of the water. For example, the dissolution of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in acidic waters, such as rainwater, can lead to the formation of bicarbonate (HCO3-) and calcium (Ca2+) ions, which can increase the pH of the water. Conversely, the presence of certain minerals, such as those in limestone, can make the water more acidic, while the presence of other minerals, such as those in granite, can make the water more alkaline.
Surrounding Environment
The surrounding environment can also influence the pH of water from metamorphic rocks. For instance, the introduction of pollutants, such as toxic metals and acid waters, can alter the pH of the water, making it more acidic or alkaline. These pollutants can enter the water through natural processes or human activities, and their presence can have negative effects on the environment and human health.
Measuring and Balancing the pH of Water from Metamorphic Rocks
Measuring and balancing the pH of water from metamorphic rocks is essential for maintaining water quality and ensuring the safety of water resources.
Measuring the pH
The pH of water from metamorphic rocks can be measured using pH test strips or pH meters, which are widely available and relatively inexpensive. These tools allow for the accurate assessment of the water’s pH, which is crucial for determining the appropriate methods for balancing the pH.
Balancing the pH
To balance the pH of water from metamorphic rocks, various methods can be used, including the addition of acid or alkali to the water. For example, the addition of lime (CaO) or soda ash (Na2CO3) can be used to raise the pH of acidic water, while the addition of hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) can be used to lower the pH of alkaline water.
Home Remedies for Balancing the pH of Water from Metamorphic Rocks
In addition to professional methods, there are also home remedies that can be used to balance the pH of water from metamorphic rocks.
Using Vinegar and Baking Soda
One simple home remedy is the use of vinegar (acetic acid) or baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) to lower or raise the pH of the water, respectively. These household items can be added to the water in small amounts until the desired pH is achieved.
Testing and Adjusting
It is important to regularly test the pH of the water and make adjustments as needed to maintain the desired pH range. This can be done using pH test strips or meters, and the appropriate amount of vinegar or baking soda can be added to the water to achieve the desired pH.
Conclusion
The pH of water from metamorphic rocks can vary widely, depending on the minerals present in the rocks and the surrounding environment. Contaminants, such as toxic metals and acid waters, can also affect the pH of the water. To maintain the quality of water from metamorphic rocks, it is essential to measure and balance the pH using appropriate methods, including the addition of acid or alkali to the water. Home remedies, such as the use of vinegar and baking soda, can also be effective in adjusting the pH of the water.
References:
– Metamorphic Rocks: An Overview
– Understanding Water Quality
– Acid Mine Drainage and its Impact on Water Quality