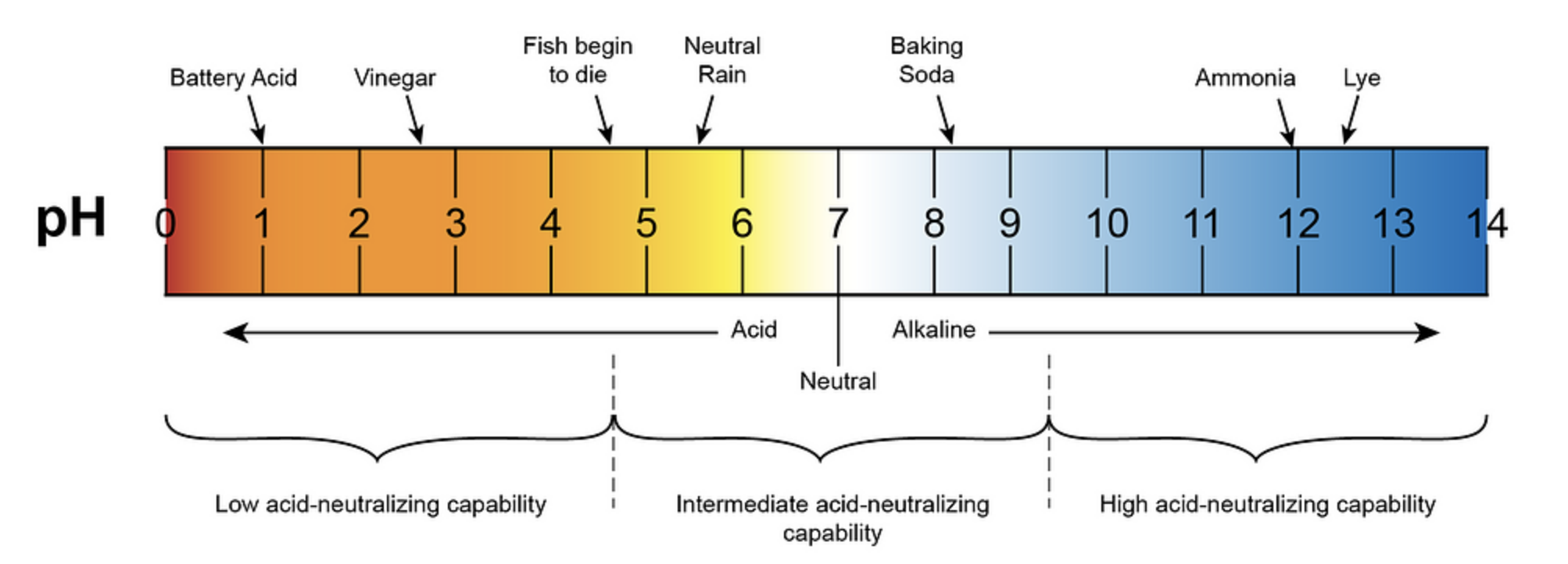
The pH of hose water is a crucial factor to consider when it comes to irrigation, gardening, and various household applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the importance of understanding the pH of hose water, the potential impacts on plants and surfaces, and practical steps to ensure optimal water quality for your needs.
Understanding the pH of Hose Water
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Water with a pH below 7 is considered acidic, while water with a pH above 7 is considered basic or alkaline. For hose water, a pH between 5.0 and 7.0 is generally recommended for optimal plant growth and overall suitability.
Measuring the pH of Hose Water
To determine the pH of your hose water, you can use a simple pH test kit. These kits typically include test strips or a digital pH meter that can be dipped directly into the water. The test results will provide you with a precise pH reading, allowing you to assess the acidity or alkalinity of your hose water.
Factors Affecting the pH of Hose Water
The pH of hose water can be influenced by several factors, including the source of the water, the materials used in the plumbing system, and any treatment or additives introduced along the way. Factors such as the presence of minerals, dissolved gases, and contaminants can all contribute to the overall pH of the water.
Impacts of pH on Plants and Surfaces
The pH of hose water can have significant implications for plant health, soil conditions, and the longevity of various surfaces and materials.
Impact on Plant Growth and Nutrition
Hose water with an unsuitable pH can affect the availability and uptake of essential nutrients by plants. Acidic water (pH below 5.0) can lead to nutrient deficiencies, while alkaline water (pH above 7.0) can cause certain nutrients to become less accessible to the plants.
Impact on Soil and Surfaces
The pH of hose water can also impact the pH of the soil, potentially leading to imbalances that can affect plant growth and soil health. Additionally, the pH of hose water can influence the longevity and appearance of various surfaces, such as concrete, stone, and metal, potentially causing discoloration or accelerated weathering.
Optimizing the pH of Hose Water
To ensure the best possible outcomes for your plants, soil, and surfaces, it’s essential to optimize the pH of your hose water.
Adjusting the pH of Hose Water
If the pH of your hose water is outside the recommended range, you can take steps to adjust it. This may involve the use of pH-adjusting chemicals, such as acids or bases, or the installation of a water treatment system that can neutralize the pH.
Monitoring and Maintaining Optimal pH
Regularly testing the pH of your hose water and making necessary adjustments is crucial for maintaining optimal conditions. This may involve periodic testing and adjustments, as well as monitoring the overall health and performance of your plants, soil, and surfaces.
Conclusion
The pH of hose water is a critical factor that can have far-reaching implications for your gardening, irrigation, and household needs. By understanding the importance of pH, measuring and monitoring the water quality, and taking appropriate steps to optimize the pH, you can ensure the best possible outcomes for your plants, soil, and surfaces. Remember, a little attention to the pH of your hose water can go a long way in maintaining a healthy, thriving environment.
References:
- Water Quality: pH and Alkalinity – UMass Extension
- pH Water Test: Is your water Alkaline or Acidic? – TEN Spring Water
- Acidic And Alkaline Water: Health Benefits And Risks – Waterdrop
- What Causes a High pH Level in Water? – Eldorado Spring Water